Mass Balancing (Two-Product Formula)
Description
This article describes the classical two-product formula for estimating the separation efficiency of a process.
Model theory
The two-product formula estimates the mass flow split of solids and the recovery of a single assayed component from a process step with one feed and two product streams.[1]
The formula is derived from a consideration of the mass balance of solids flow and the assayed component around the process. That is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ Ff = Cc + Tt }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math] are the mass flow rates of the feed, concentrate and tailings streams, respectively.
- [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ t }[/math] are the assay values of a single component in the feed, concentrate and tailings streams, respectively.
By rearranging the two-product mass balance equation, the solids split to concentrate is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ S = \dfrac{C}{F} = \dfrac{f - t}{c - t} }[/math]
Then, the recovery of the single assay component to concentrate is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ R = S \left ( \dfrac{c}{f} \right ) = \left ( \dfrac{f - t}{c - t} \right ) \left ( \dfrac{c}{f} \right ) }[/math]
The impact of assay measurement errors on the calculated solids split and recovery can be approximated by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\sigma_S}^2 = \left (\dfrac{1}{c - t} \right )^2 {\sigma_f}^2 + \left (\dfrac{f - t}{(c - t)^2} \right )^2 {\sigma_c}^2 + \left (\dfrac{c - f}{(c - t)^2} \right )^2 {\sigma_t}^2 }[/math]
and
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\sigma_R}^2 = \dfrac{{c}^2 {t}^2}{{f}^2 (c - t)^4} \left [ \dfrac{(c - t)^2}{{f}^2}{\sigma_f}^2 + \dfrac{(f - t)^2}{{c}^2}{\sigma_c}^2 + \dfrac{(c - f)^2}{{t}^2}{\sigma_t}^2\right ] }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_S }[/math] is the estimated standard deviation of the solids split (frac)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_R }[/math] is the estimated standard deviation of the assayed component recovery (frac)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_f }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_c }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma_t }[/math] are the standard deviations of the measurement error associated with the assayed component of the feed, concentrate and tailings streams, respectively.
The assays must show a reasonable degree of degree of separation across the process for the two-product formula to return sensible results.
Mineral compositions, particle size distributions and water fractions can be substituted in place of metal assays in the formula.
Excel
The two-product formula may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function call:
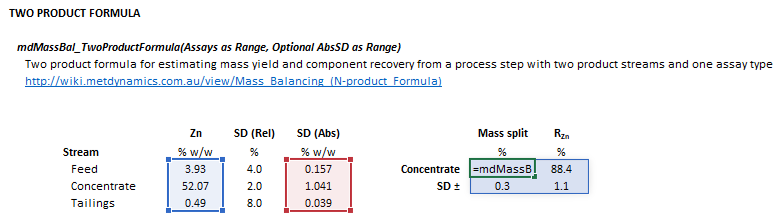
=mdMassBal_TwoProductFormula(Assay as Range, Optional AbsSD as Range)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
|
| ||||
See also
References
- ↑ Wills, B.A. and Napier-Munn, T.J., 2005. Wills' Mineral Processing Technology (Seventh Edition). Butterworth-Heinemann.