Time Series Analysis (Moving Average Filters)
Description
This article describes several filters for the analysis of time series data, including:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Linear Regression Moving Average (LRMA)
Model theory
Simple moving average
Exponential moving average
Linear regression moving average
Excel
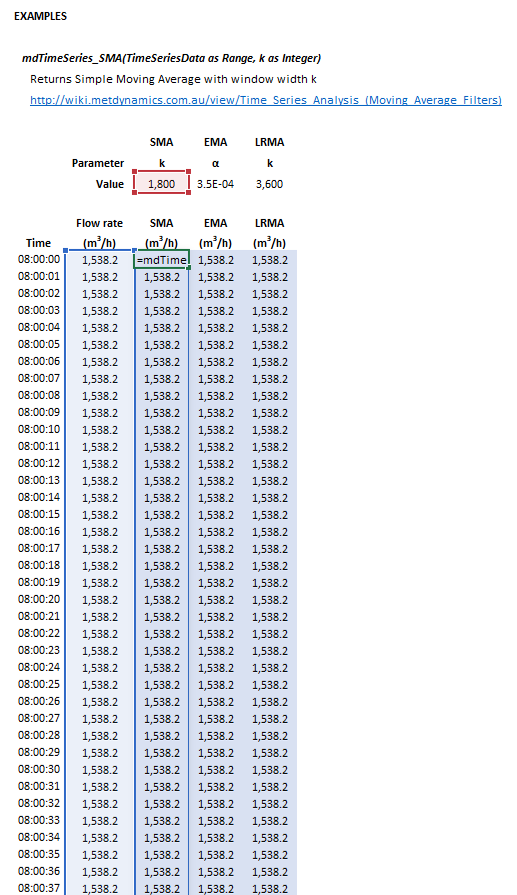
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) filter may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdTimeSeries_SMA(TimeSeriesData as Range, k as Integer)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
| ||||
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) filter may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdTimeSeries_EMA(TimeSeriesData as Range, alpha as Double)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
| ||||
The Linear Regression Moving Average (LRMA) filter may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdTimeSeries_LRMA(TimeSeriesData as Range, k as Integer)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
| ||||