Revision as of 06:18, 18 May 2023 by md>Scott.Munro
Description
This article describes methods for estimating particle size distributions using the Gaudin-Schuhmann, Rosin-Rammler and Swebrec equations.[1][2]
Model theory
 This section is currently under construction. Please check back later for updates and revisions. This section is currently under construction. Please check back later for updates and revisions.
|
Excel
Gaudin-Schuhmann
The Gaudin-Schuhmann distribution may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdDist_GaudinSchuhmann(Size as Range, k as Double, m as Double)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{Size} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
d_1\text{ (mm)}\\
\vdots\\
d_n\text{ (mm)}\\
\end{bmatrix}\\
\\
\mathit{k} & = \big [ k\text{ (mm)} \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{a} & = \big [ a \big ]
\end{align} }[/math]
|
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{mdDist\_GaudinSchuhmann} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
P_1\text{ (frac)}\\
\vdots\\
P_n\text{ (frac)}\\
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align}
}[/math]
|
|
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_i }[/math] is the size of the square mesh interval that feed mass is retained on (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_{i+1}\lt d_i\lt d_{i-1} }[/math], i.e. descending size order from top size ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{1} }[/math]) to sub mesh ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{n}=0 }[/math] mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] is the size parameter (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ a }[/math] is the distribution parameter
- [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math] is the cumulative quantity passing size interval [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math]
|
|
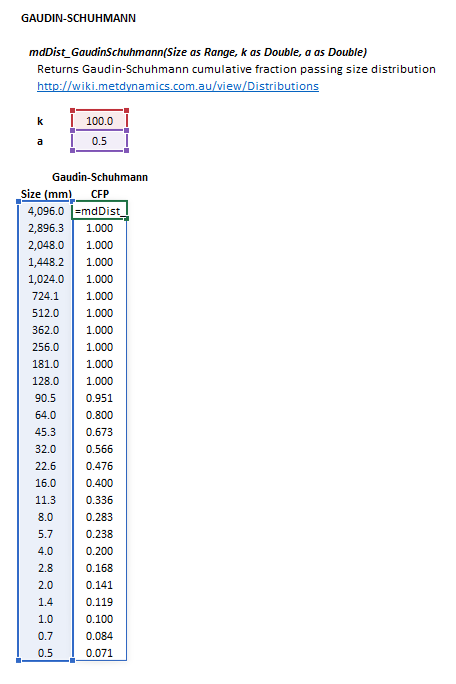 Figure 1. Example showing the selection of the Size (blue frame), k (red frame), a (purple frame) and Results (light blue frame) arrays in Excel.
|
Rosin-Rammler
The Rosin-Rammler distribution may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdDist_RosinRammler(Size as Range, x1 as Double, b as Double)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{Size} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
d_1\text{ (mm)}\\
\vdots\\
d_n\text{ (mm)}\\
\end{bmatrix}\\
\\
\mathit{x1} & = \big [ x^1\text{ (mm)} \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{b} & = \big [ b \big ]
\end{align} }[/math]
|
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{mdDist\_RosinRammler} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
P_1\text{ (frac)}\\
\vdots\\
P_n\text{ (frac)}\\
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align}
}[/math]
|
|
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_i }[/math] is the size of the square mesh interval that feed mass is retained on (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_{i+1}\lt d_i\lt d_{i-1} }[/math], i.e. descending size order from top size ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{1} }[/math]) to sub mesh ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{n}=0 }[/math] mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ x^1 }[/math] is the size parameter (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] is the distribution parameter
- [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math] is the cumulative quantity passing size interval [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math]
|
|
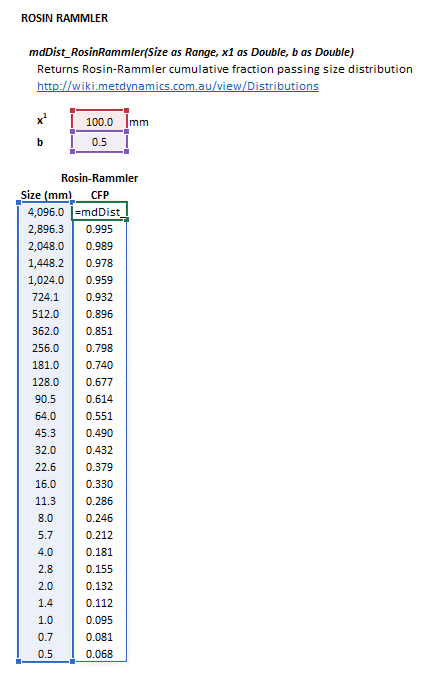 Figure 2. Example showing the selection of the Size (blue frame), x1 (red frame), b (purple frame) and Results (light blue frame) arrays in Excel.
|
Swebrec
The Swebrec distribution may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function calls:
=mdDist_Swebrec(Size as Range, xMax as Double, x50 as Double, b as Double, Optional a as Double = 0, Optional c as Double = 0)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
The input parameters and calculation results are defined below in matrix notation, along with an example image showing the selection of the same cells and arrays in the Excel interface:
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{Size} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
d_1\text{ (mm)}\\
\vdots\\
d_n\text{ (mm)}\\
\end{bmatrix}\\
\\
\mathit{xMax} & = \big [ x_{\rm Max}\text{ (mm)} \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{x50} & = \big [ x_{50}\text{ (mm)} \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{b} & = \big [ b \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{a} & = \big [ a \big ]\\
\\
\mathit{c} & = \big [ c \big ]
\end{align} }[/math]
|
- [math]\displaystyle{
\begin{align}
\mathit{mdDist\_Swebrec} & =
\begin{bmatrix}
P_1\text{ (frac)}\\
\vdots\\
P_n\text{ (frac)}\\
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align}
}[/math]
|
|
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_i }[/math] is the size of the square mesh interval that feed mass is retained on (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_{i+1}\lt d_i\lt d_{i-1} }[/math], i.e. descending size order from top size ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{1} }[/math]) to sub mesh ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{n}=0 }[/math] mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_{\rm Max} }[/math] is the maximum (top) size of the distribution (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_{50} }[/math] is the mean size (passing 50%) of the distribution (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] is a curve-undulation exponent
- [math]\displaystyle{ a }[/math] is an optional proportion parameter (default is zero if omitted)
- [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is an optional undulation exponent (default is zero if omitted)
- [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math] is the cumulative quantity passing size interval [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math]
|
|
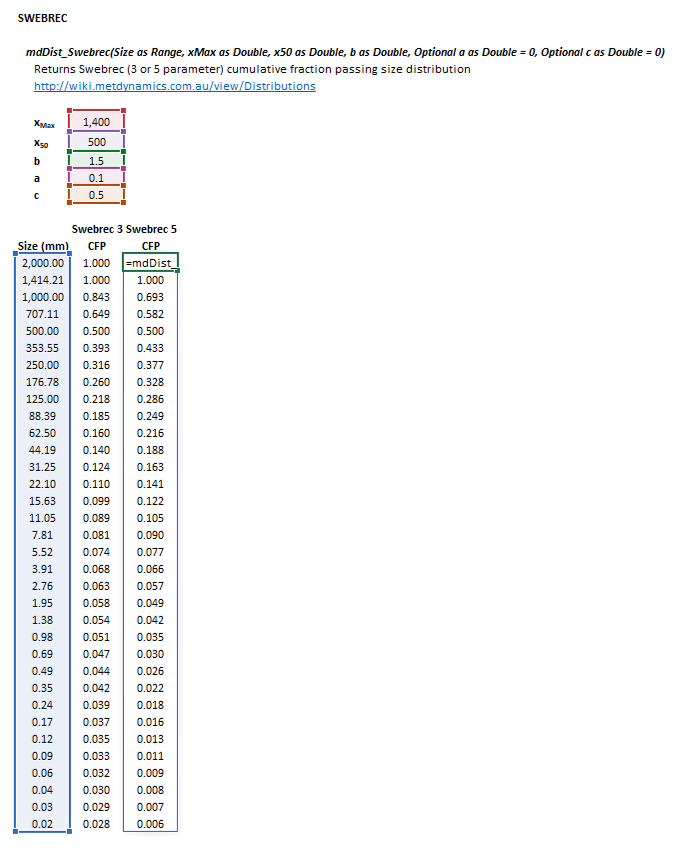 Figure 3. Example showing the selection of the Size (blue frame), xMax (red frame), x50 (purple frame), b (green frame),a (pink frame), c (brown frame) and Results (light blue frame) arrays in Excel.
|
References
- ↑ Gupta, A. and Yan, D.S., 2016. Mineral processing design and operations: an introduction. Elsevier.
- ↑ Ouchterlony, F., 2005. The Swebrec© function: linking fragmentation by blasting and crushing. Mining Technology, 114(1), pp.29-44.


