Fine Wet Screen (Mwale): Difference between revisions
imported>Scott.Munro m (→See also) Tag: Reverted |
imported>Scott.Munro m (Undo revision 10675 by Scott.Munro (talk)) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<hide> | <hide> | ||
=== Efficiency curve === | |||
Mwale et al. (2016) proposed a phenomenological model of fine wet screening where the partition to oversize, <math>E_{i{\rm o}}</math> (frac), is related to properties of both the screen and the feed:{{Mwale et al. (2016)}} | |||
:<math>E_{i{\rm o}} = \exp \left [ - \dfrac{A_{\rm o} K}{F_{\rm f} s \left ( \dfrac{\bar d_i}{a} \right)^\alpha} \right ] + \dfrac{\delta . F_{\rm f}}{100(1-s)} \left [ \exp \left ( - \dfrac{\bar d_i}{a} \right ) \right ]^\alpha</math> | |||
where: | |||
* <math>A_{\rm o}</math> is the total screen open area (m<sup>2</sup>) | |||
* <math>F_{\rm f}</math> is the solids feed rate (t/h) | |||
* <math>s</math> is the mass fraction of solids in the feed (w/w) | |||
* <math>x_{\rm a}</math> is the aperture size (mm) | |||
* <math>\bar d_{i}</math> is the [[Conversions|geometric mean size]] of the size interval <math>i</math> (mm) | |||
* <math>K</math> is the kinetic constant (t/hr.m<sup>2</sup>) | |||
* <math>\alpha</math> is the sharpness of separation parameter (-) | |||
* <math>\delta</math> is the fines bypass parameter (h/t) | |||
=== Sharpness constant === | |||
Mwale et al. (2018) suggest the following equation to estimate the sharpness constant, <math>\alpha</math>, as a function of screen design and feed conditions:{{Mwale et al. (2018)}} | |||
:<math>\ | :<math>\alpha = k_1 \left ( \dfrac{{\rho_{\rm p}}^2 F_{\rm f} {A_{\rm o}}^{3.5}}{\mu a^2 {M_{\rm u}}^2} \right ) + k_2 \left ( \dfrac{A_{\rm o}}{a^2} \right ) + k_3</math> | ||
where: | |||
* <math> | * <math>\rho_{\rm p}</math> is the density of the feed slurry (t/m<sup>3</sup>) | ||
* <math>M_{\rm u}</math> is the mass flow rate of particles in the feed which are smaller than the aperture (t/h) | |||
* <math>k_1</math>, <math>k_2</math> and <math>k_3</math> are coefficients of the sharpness equation | |||
* <math> | |||
* <math> | |||
The apparent viscosity of slurry in the feed, <math>\mu</math> (Pa.s), is estimated by the classical Krieger-Dougherty (1959) equation:{{Krieger and Dougherty (1959)}} | |||
:<math>\mu = \mu_{\rm 0} \left ( 1 - \dfrac{\phi_{\rm Eff}}{\phi_{\rm m}} \right)^{-k \phi_{\rm m}}</math> | |||
where: | where: | ||
* <math>\ | * <math>\mu_0</math> is the viscosity of the carrier fluid, i.e. water (Pa.s) | ||
* <math>\ | * <math>\phi_{\rm m}</math> is maximum packing fraction of particles (v/v), assumed to be 0.64 | ||
* <math>k</math> is a particle shape constant, assumed to be 2.5 | |||
* <math> | |||
The sharpness constant can be specified directly as the value of coefficient <math>k_3</math> when coefficients <math>k_1</math> and <math>k_2</math> are set to zero. | |||
=== Bypass constant === | |||
Mwale et al. (2018) suggest the following simple linear relationship to estimate the bypass constant, <math>\delta</math>,:{{Mwale et al. (2018)}} | |||
:<math> | :<math>\delta = C_1.F_{\rm f} + C_2.s + C_3.x_{\rm a} + C_4</math> | ||
where | where <math>C_1-C_4</math> are coefficients of the bypass equation. | ||
The bypass constant can be specified directly as the value of coefficient <math>C_4</math> when coefficients <math>C_1-C_3</math> are set to zero. | |||
</hide> | </hide> | ||
Revision as of 01:50, 15 October 2025
Description
This article describes an implementation of the Mwale et al. (2016) model for fine wet screening.[1]
Model theory
Excel
The Mwale fine wet screen model may be invoked from the Excel formula bar with the following function call:
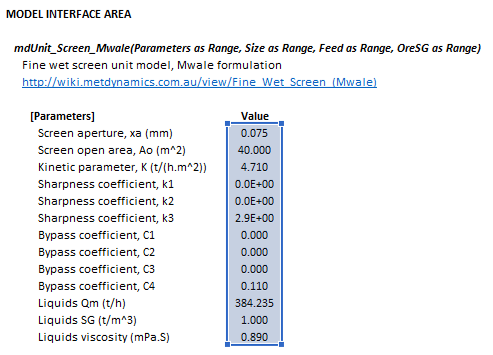
=mdUnit_Screen_Mwale(Parameters as Range, Size as Range, Feed as Range, OreSG as Range)
Invoking the function with no arguments will print Help text associated with the model, including a link to this page.
Inputs
The required inputs are defined below in matrix notation with elements corresponding to cells in Excel row ([math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math]) x column ([math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math]) format:
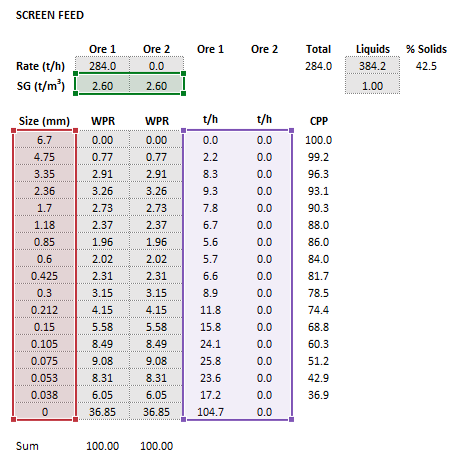
- [math]\displaystyle{ Parameters= \begin{bmatrix} x_{\rm a} \text{ (mm)}\\ A_{\rm o}\text{ (m}^2\text{)}\\ K\text{ (t/h.m}^2\text{)}\\ k_1\text{ (-)}\\ k_2\text{ (-)}\\ k_3\text{ (-)}\\ C_1\text{ (-)}\\ C_2\text{ (-)}\\ C_3\text{ (-)}\\ C_4\text{ (-)}\\ (Q_{\rm M,F})_{\rm L}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \rho_{\rm L}\text{ (t/m}^{\text{3}}\text{)}\\ \mu_0\text{ (mPa.S)}\\ \end{bmatrix},\;\;\;\;\;\; Size = \begin{bmatrix} d_{1}\text{ (mm)}\\ \vdots\\ d_n\text{ (mm)}\\ \end{bmatrix},\;\;\;\;\;\; Feed= \begin{bmatrix} (Q_{\rm M,F})_{11}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,F})_{1m}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ (Q_{\rm M,F})_{n1}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,F})_{nm}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \end{bmatrix},\;\;\;\;\;\; \mathit{OreSG}= \begin{bmatrix} (\rho_{\rm S})_1\text{ (t/m}^\text{3}\text{)} & \dots & (\rho_{\rm S})_m\text{ (t/m}^\text{3}\text{)}\\ \end{bmatrix} }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is the number of size intervals
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_i }[/math] is the size of the square mesh interval that feed mass is retained on (mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ d_{i+1}\lt d_i\lt d_{i-1} }[/math], i.e. descending size order from top size ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{1} }[/math]) to sub mesh ([math]\displaystyle{ d_{n}=0 }[/math] mm)
- [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is the number of ore types
- [math]\displaystyle{ Q_{\rm M,F} }[/math] is feed solids mass flow rate by size and ore type (t/h)
- [math]\displaystyle{ (Q_{\rm M,F})_{\rm L} }[/math] is the mass flow feed rate of liquids in the feed (t/h)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_{\rm S} }[/math] is the density of solids in the feed (t/m3)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_{\rm L} }[/math] is the density of liquids in the feed (t/m3)
Results
The results are displayed in Excel as an array corresponding to the matrix notation below:
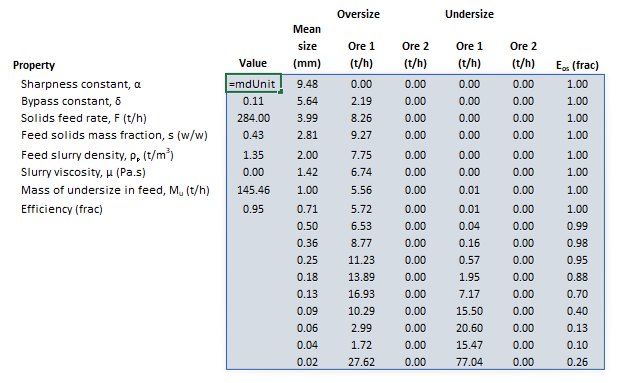
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathit{mdUnit\_Screen\_Mwale} = \begin{bmatrix} \begin{array}{c} \begin{bmatrix} \alpha\text{ (-)}\\ \delta\text{ ((t/h)}^{-1}\text{)}\\ F_{\rm f}\text{ (t/h)}\\ s\text{ (w/w)}\\ \rho_{\rm p}\text{ (t/m}^3\text{)}\\ \mu\text{ (Pa.s)}\\ M_{\rm u}\text{ (t/h)}\\ E_{\rm US}\text{ (frac)}\\ \end{bmatrix} \end{array} \begin{array}{cccccc} \begin{bmatrix} \bar d_1\text{ (mm)}\\ \vdots\\ \bar d_n\text{ (mm)} \end{bmatrix} & \begin{bmatrix} (Q_{\rm M,OS})_{11}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,OS})_{1m}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ (Q_{\rm M,OS})_{n1}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,OS})_{nm}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \end{bmatrix} & \begin{bmatrix} (Q_{\rm M,US})_{11}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,US})_{1m}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ (Q_{\rm M,US})_{n1}\text{ (t/h)} & \dots & (Q_{\rm M,US})_{nm}\text{ (t/h)}\\ \end{bmatrix} & \begin{bmatrix} (E_{i \rm o})_1\text{ (frac)}\\ \vdots\\ (E_{i \rm o})_n\text{ (frac)} \end{bmatrix} \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \end{array} \end{bmatrix} }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ E_{\rm US} }[/math] is the efficiency of undersize removal achieved by the screen (frac)
- [math]\displaystyle{ Q_{\rm M,OS} }[/math] is mass flow rate of solids to the oversize stream (t/h)
- [math]\displaystyle{ Q_{\rm M,US} }[/math] is mass flow rate of solids to the undersize stream (t/h)
Example
The images below show the selection of input arrays and output results in the Excel interface.
SysCAD
The sections and variable names used in the SysCAD interface are described in detail in the following tables.
Note that a Deck and Partition page is provided for each connected oversize discharge stream.
MD_Screen page
The first tab page in the access window will have this name.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Display | Description/Calculated Variables/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Tag | Display | This name tag may be modified with the change tag option. |
| Condition | Display | OK if no errors/warnings, otherwise lists errors/warnings. |
| ConditionCount | Display | The current number of errors/warnings. If condition is OK, returns 0. |
| GeneralDescription / GenDesc | Display | This is an automatically generated description for the unit. If the user has entered text in the 'EqpDesc' field on the Info tab (see below), this will be displayed here.
If this field is blank, then SysCAD will display the unit class ID. |
| Requirements | ||
| On | CheckBox | This enables the unit. If this box is not checked, then the MassFracToOS option appears below. |
| MassFracToOS | Input | Only appears if the On field above is not checked. Specifies the fraction of feed mass that reports to the overflow stream when the model is off. |
| NumParallelUnits | Input | The number of parallel, identical units to simulate:
|
| Options | ||
| ShowQFeed | CheckBox | QFeed and associated tab pages (eg Sp) will become visible, showing the properties of the combined feed stream. |
| SizeForPassingFracCalc | Input | Size fraction for % Passing calculation. The size fraction input here will be shown in the Stream Summary section. |
| FracForPassingSizeCalc | Input | Fraction passing for Size calculation. The fraction input here will be shown in the Stream Summary section. |
| Stream Summary | ||
| MassFlow / Qm | Display | The total mass flow in each stream. |
| SolidMassFlow / SQm | Display | The Solids mass flow in each stream. |
| LiquidMassFlow / LQm | Display | The Liquid mass flow in each stream. |
| VolFlow / Qv | Display | The total Volume flow in each stream. |
| Temperature / T | Display | The Temperature of each stream. |
| Density / Rho | Display | The Density of each stream. |
| SolidFrac / Sf | Display | The Solid Fraction in each stream. |
| LiquidFrac / Lf | Display | The Liquid Fraction in each stream. |
| Passing | Display | The mass fraction passing the user-specified size (in the field SizeForPassingFracCalc) in each stream. |
| Passes | Display | The user-specified (in the field FracForPassesSizeCalc) fraction of material in each stream will pass this size fraction. |
Deck page
The Deck page is used to specify the required model method and associated input parameters.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Display | Description/Calculated Variables/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Deck | ||
| On | Checkbox | This enables the deck. If off, the feed to this deck passes directly to the next deck (or undersize) without partition. |
| Method | Partition (User) | The partition to oversize for each size interval is defined by the user. Different values can be used for different solids. |
| Partition (Reid-Plitt) | The partition to oversize for each size interval is defined by a Reid-Plitt efficiency curve. Different parameters can be used for different solids. | |
| Partition (Whiten-Beta) | The partition to oversize for each size interval is defined by a Whiten-Beta efficiency curve. Different parameters can be used for different solids. | |
| Vibrating (Karra) | The Karra vibrating screen model is used to determine the partition of solids to oversize and undersize for each size interval. | |
| Vibrating (Whiten) | The Whiten vibrating screen model is used to determine the partition of solids to oversize and undersize for each size interval. | |
| Vibrating (Metso) | The Metso vibrating screen model is used to determine the partition of solids to oversize and undersize for each size interval. | |
| Fine Wet (Mwale) | The Mwale fine wet screen model is used to determine the partition of solids to oversize and undersize for each size interval. | |
| Dewatering (Ng) | The Ng dewatering screen model is used to determine the moisture content of oversize material, and the partition of solids to oversize and undersize for each size interval. | |
| HelpLink | Opens a link to this page using the system default web browser. Note: Internet access is required. | |
| Parameters | ||
| Aperture / xa | Input | Size of the apertures in the deck. |
| OpenArea/ Ao | Input | Open area of the screening surface |
| KineticParameter / K | Input | Mwale model kinetic parameter |
| SharpnessCoeff1 / k1 | Input | Mwale model sharpness coefficient |
| SharpnessCoeff2 / k2 | Input | Mwale model sharpness coefficient |
| SharpnessCoeff3 / k3 | Input | Mwale model sharpness coefficient |
| BypassCoeff1 / C1 | Input | Mwale model bypass coefficient |
| BypassCoeff2 / C2 | Input | Mwale mode3 bypass coefficient |
| BypassCoeff3 / C3 | Input | Mwale model bypass coefficient |
| BypassCoeff4 / C4 | Input | Mwale model bypass coefficient |
| Liquids | ||
| LiquidsSeparMethod | Split To OS (User) | Liquids are split to oversize by a user-defined fraction of liquids in the feed. |
| OS Solids Fraction | Sufficient liquids mass is recovered to the oversize stream to yield the user-defined oversize solids mass fraction value (if possible). | |
| OS Liquids Fraction | Sufficient liquids mass is recovered to the oversize stream to yield the user-defined oversize liquids mass fraction value (if possible). | |
| OSSolidsFracReqd / OS.SfReqd | Input | Required value of the mass fraction of solids in the oversize stream. Only visible if OS Solids Fraction is selected. |
| OSLiquidsFracReqd / OS.LfReqd | Input | Required value of the mass fraction of liquids in the oversize stream. Only visible if OS Liquids Fraction is selected. |
| LiqSplitToOS / OS.LiqSplit | Input/Display | The fraction of feed liquids recovered to the oversize stream. |
| Results | ||
| SharpnessConstant / Alpha | Display | Mwale model sharpness constant |
| BypassConstant / Delta | Display | Mwale model bypass constant |
| Feed.SQm | Display | Mass flow rate of solids in the feed (excludes solids without PSD quality) |
| Feed.SQmSubAp | Display | Mass flow rate of particles in the feed which are smaller than the aperture size (sub-aperture) |
| Feed.Sf | Display | Mass fraction of solids in the feed (excludes solids without PSD quality) |
| Feed.SLRho | Display | Density of slurry in the feed |
| SlurryViscosity / mu | Display | Apparent viscosity of slurry in the feed |
| Efficiency | Display | Fraction of total sub-aperture sized material in feed that is actually recovered to the undersize stream. |
Partition page
The Partition page is used to display (or specify) the partition by species/component/element/individual phase and size values.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Display | Description/Calculated Variables/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | ||
| Name | Display | Shows the name of the SysCAD Size Distribution (PSD) quality associated with the feed stream. |
| IntervalCount | Display | Shows the number of size intervals in the SysCAD Size Distribution (PSD) quality associated with the feed stream. |
| SpWithPSDCount | Display | Shows the number of species in the feed stream assigned with the SysCAD Size Distribution (PSD) quality. |
| Partition | ||
| Method | Model / User | Select model-calculated or user-defined partition to separate each solids species type. |
| Density | Display | Density of each solid species. |
| Size | Display | Size of each interval in mesh series. |
| MeanSize | Display | Geometric mean size of each interval in mesh series.
|
| All (All column) | Display |
|
| Partition | Display |
|
| All (All row, All column) | Display |
|
| All (All row, per species) | Display |
|
| CmpPartition | ||
| Components | Hides or shows component partition table. | |
| Size | Display | Size of each interval in mesh series. |
| MeanSize | Display | Geometric mean size of each interval in mesh series. |
| All (All column) | Display |
|
| CmpPartition | Display |
|
| All (All row, All column) | Display |
|
| All (All row, per component) | Display |
|
| ElePartition | ||
| Elements | Hides or shows element partition table. | |
| Size | Display | Size of each interval in mesh series. |
| MeanSize | Display | Geometric mean size of each interval in mesh series. |
| All (All column) | Display |
|
| ElePartition | Display |
|
| All (All row, All column) | Display |
|
| All (All row, per element) | Display |
|
| IPhPartition | ||
| IPhases | Hides or shows individual phases partition table. | |
| Size | Display | Size of each interval in mesh series. |
| MeanSize | Display | Geometric mean size of each interval in mesh series. |
| All (All column) | Display |
|
| IPhPartition | Display |
|
| All (All row, All column) | Display |
|
| All (All row, per individual phase) | Display |
|
About page
This page is provides product and licensing information about the Met Dynamics Models SysCAD Add-On.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Display | Description/Calculated Variables/Options |
|---|---|---|
| About | ||
| HelpLink | Opens a link to the Installation and Licensing page using the system default web browser. Note: Internet access is required. | |
| Information | Copies Product and License information to the Windows clipboard. | |
| Product | ||
| Name | Display | Met Dynamics software product name |
| Version | Display | Met Dynamics software product version number. |
| BuildDate | Display | Build date and time of the Met Dynamics Models SysCAD Add-On. |
| License | ||
| File | This is used to locate a Met Dynamics software license file. | |
| Location | Display | Type of Met Dynamics software license or file name and path of license file. |
| SiteCode | Display | Unique machine identifier for license authorisation. |
| ReqdAuth | Display | Authorisation level required, MD-SysCAD Full or MD-SysCAD Runtime. |
| Status | Display | License status, LICENSE_OK indicates a valid license, other messages report licensing errors. |
| IssuedTo | Display | Only visible if Met Dynamics license file is used. Name of organisation/seat the license is authorised to. |
| ExpiryDate | Display | Only visible if Met Dynamics license file is used. License expiry date. |
| DaysLeft | Display | Only visible if Met Dynamics license file is used. Days left before the license expires. |
Additional notes
- Solid species that do not possess a particle size distribution property are split according to the overall mass split of the default particle size distribution species selected in the SysCAD Project Configuration.
- If the default particle size distribution species is not present in the unit feed, the overall split of all other species with particle size distributions combined is used, as determined by the model.
- Gas phase species report directly to the undersize stream without split.
External links
References
- ↑ Mwale, A.N., Mainza, A.N., Bepswa, P.A., Simukanga, S., Masinja, J.H., 2016. MODEL FOR FINE WET SCREENING. In XXVIII International Mineral Processing Congress Proceedings. Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum.